Setting Up a Factorial Experiment Psychology Research Methods
Table Of Content
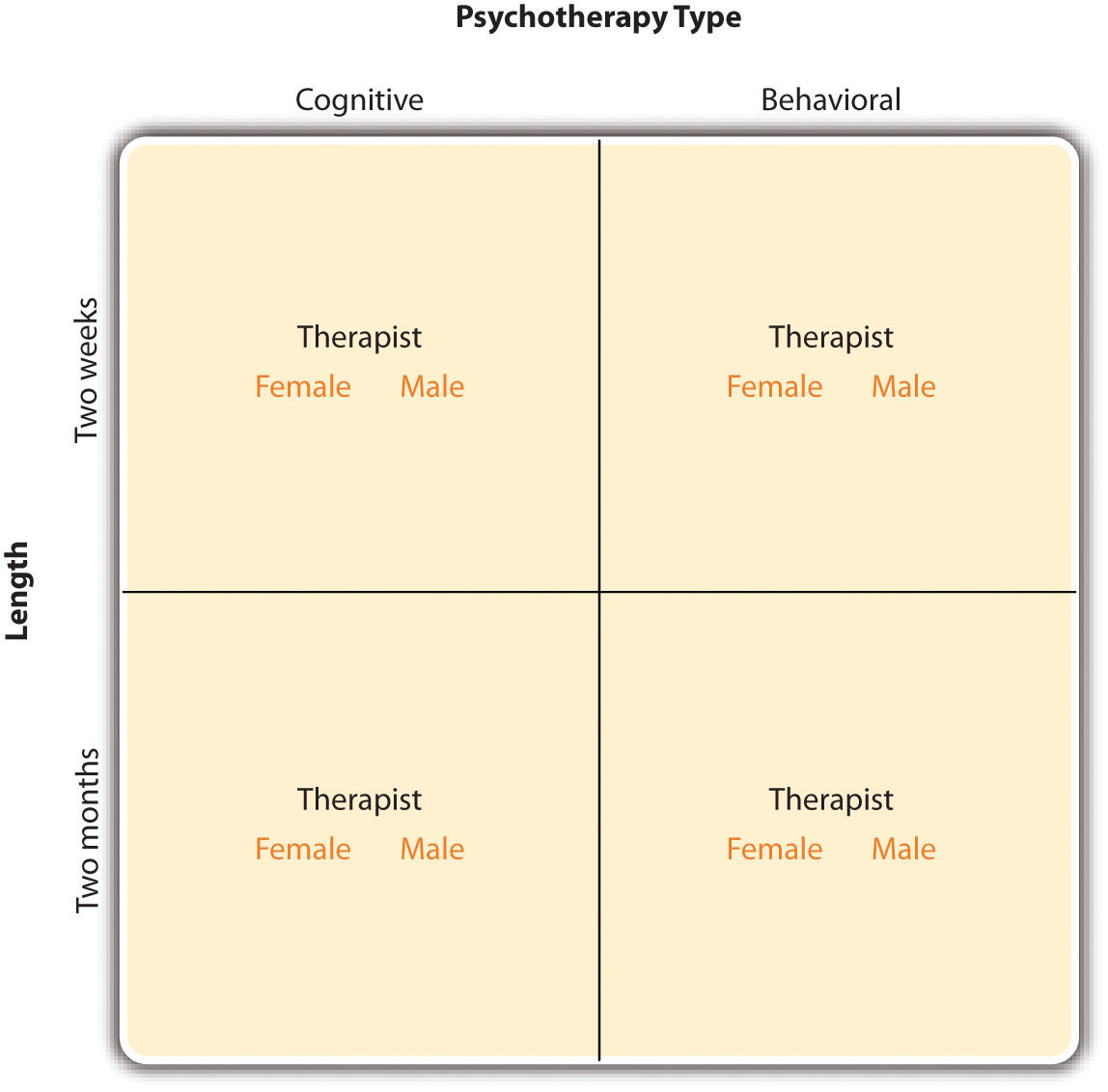
The table below shows how to construct F ratios when an experiment uses a Random-effects model. The table below shows how to construct F ratios when an experiment uses a fixed-effects model. All three of these residuals versus the main effects show same pattern, the large predicted values tend to have larger variation. A transformation - the large values are more variable than smaller values.
Understanding Main Effects?
The first independent variable will be time since last meal (1 hour vs. 5 hours), and the second independent variable will be how tired someone is (not tired vs very tired). When researchers combine dependent variables in this way, they are treating them collectively as a multiple-response measure of a single construct. The advantage of this is that multiple-response measures are generally more reliable than single-response measures.

When to use Experimental Research Design
You would measure combination effects of \(A\) and \(B\) (a1b1, a1b2, a2b1, a2b2). Since we have two factors, each of which has two levels, we say that we have a 2 x 2 or a 22 factorial design. Typically, when performing factorial design, there will be two levels, and n different factors. Experiments that include more than one independent variable in which each level of one independent variable is combined with each level of the others to produce all possible combinations. In the first study, participants were randomly assigned to receive either 3 weeks of light flashes (light alone) or a sham light intervention. The light flashes were brief light pulses administered in 3-millisecond bursts delivered 20 seconds apart, starting 3 hours before the targeted wake time for the individual participant.
Purpose of Experimental Design
The statistical analyses would reveal whether the experimental treatment “package” differs in effects from the usual care treatment. However, conducting an RCT that comprises ICs whose joint effects are unknown, poses clear risks. This is because research shows that the effectiveness of a IC can be substantially modulated by the other ICs with which it is used (Cook et al., 2016; Fraser et al., 2014; Schlam et al., 2016); i.e., they may interact. A 2×2 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables (each with two levels) on a single dependent variable. The number of ICs may affect the clinical relevance and generalizability of the research findings.
Interaction Effects
Flexible experimental designs for valid single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments allowing batch effects correction - Nature.com
Flexible experimental designs for valid single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments allowing batch effects correction.
Posted: Wed, 01 Jul 2020 07:00:00 GMT [source]
As most of you know from regression the further apart your two points are the less variance there is in the estimate of the slope. The variance of the slope of a regression line is inversely related the distance between the extreme points. You can reduce this variance by choosing your high and low levels far apart. To summarize what we have learned in this lesson thus far, we can write a contrast of the totals which defines an effect, we can estimate the variance for this effect and we can write the sum of squares for an effect. We can do this very simply using Yates notation which historically has been the value of using this notation. The sum of the products of the contrast coefficients times the totals will give us an estimate of the effects.
They measured their participants’ SES and had them play the “dictator game.” They told participants that each would be paired with another participant in a different room. (In reality, there was no other participant.) Then they gave each participant 10 points (which could later be converted to money) to split with the “partner” in whatever way he or she decided. Because the participants were the “dictators,” they could even keep all 10 points for themselves if they wanted to. When the independent variable is a construct that can only be manipulated indirectly—such as emotions and other internal states—an additional measure of that independent variable is often included as a manipulation check. This is done to confirm that the independent variable was, in fact, successfully manipulated.
Notes
However the other two combinations, A and C and A and D, indicate that significant interaction exists. If you just looked at the main effects plot you would likely miss the interactions that are obvious here. We need to think about where the variation occurs within this design.
Experiment Design Guidelines for Product Analysts — Part 1/3 - ResearchGate
Experiment Design Guidelines for Product Analysts — Part 1/3.
Posted: Mon, 21 Jun 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Look first at the effect of being tired only for the “1 hour condition”. We see the red bar (tired) is 1 unit lower than the green bar (not tired). So, there is an effect of 1 unit of being tired in the 1 hour condition.
Privileging Main Effects
The exact same patterns of data plotted up in bar graph format, are plotted as line graphs for your viewing pleasure. Note that for the IV1 graph, the red line does not appear because it is hidden behind the green line (the points for both numbers are identical). From this table, we can see that there is positive correlation for factors A and C, meaning that more sleep and more studying leads to a better test grade in the class. Factor B, however, has a negative effect, which means that spending time with your significant other leads to a worse test score. The lesson here, therefore, is to spend more time sleeping and studying, and less time with your boyfriend or girlfriend.
For each factor, you see that the residuals are more dispersed (higher variance) to the right than to the left. Overall, however, the residuals do not look too bad and the normal plot also does not look too bad. When we look at the p-values we find that A and C are significant but B and D are not. It is this course author's experience many times you can find a transformation when you have this kind of pattern. Also, sometimes when you have unequal variance you just have a couple of bad outliers, especially when you only have one or a few observations per cell. In this case it is difficult to the distinguish whether you have a couple of outliers or the data is heteroscedastic - it is not always clear.
In contrast, for interaction effect graphs, you will see that the lines are not parallel. The different ICs when used in real world settings would entail different amounts of contact or different delivery routes and their net real world effects would reflect these influences. Thus, it is important to recognize that such effects do not really constitute experimental artifacts, but rather presage the costs of complex treatments as used in real world application, presumably something worth knowing. The use of a control group is an important experimental design method that involves having a group of participants that do not receive the treatment or intervention being studied. The control group is used as a baseline to compare the effects of the treatment group. We've used Minitab to create the factorial design and added the data from the experiment into the Minitab worksheet.
Therefore, finding that several combinations of ICs yield promising effects is compatible with the goal of a screening experiment, which is to distill the number of ICS to those holding relatively great promise. In keeping with this, the data in Figure 1 suggest that we can winnow potentially promising combinations from 16, to 3. Which one of those three might be deemed most promising might be addressed via other criteria (effects on abstinence, costs, and so on) and in a follow-up RCT. Finally, including numerous ICs in an experiment could cause staff or counselors to spontaneously adjust their delivery of an intervention component because of their awareness of the total intensity of treatment provided to a participant. Counselors could either reduce the intensity of an intervention component when it is one of many that a participant receives, or they could increase the intensity of an intervention component if the participant is receiving little other treatment.
Let's use the dataset (Ex6-2.csv) and work at finding a model for this data with Minitab... In the example that was shown above, we did not randomize the runs but kept them in standard order for the purpose of seeing more clearly the order of the runs. In practice, you would want to randomize the order of run when you are designing the experiment.
Comments
Post a Comment